MLOPS Architecture
Introduction to MLOps Architecture
MLOps (Machine Learning Operations) is a structured and disciplined methodology that integrates machine learning, DevOps, and data engineering practices to manage the complete lifecycle of machine learning models in production environments. It establishes standardized processes, tools, and governance mechanisms that enable teams to move beyond experimentation and deliver scalable, reliable, and maintainable ML solutions.
A well-defined MLOps architecture provides a comprehensive framework for designing, developing, deploying, monitoring, and maintaining machine learning models with operational efficiency. It ensures seamless collaboration between data scientists, ML engineers, and operations teams by automating workflows such as data ingestion, model training, validation, deployment, and continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD). This automation reduces manual intervention, minimizes errors, and accelerates time-to-market.
As machine learning systems transition from proof-of-concept stages to business-critical applications, MLOps architecture plays a vital role in ensuring consistency, reproducibility, and governance across environments. It enables version control for data, code, and models, supports continuous monitoring for model performance and data drift, and facilitates rapid retraining and rollback when required. Ultimately, a robust MLOps architecture enhances operational stability, improves model reliability, and empowers organizations to scale machine learning initiatives confidently and sustainably.
Overview of MLOps and Its Importance
MLOps plays a critical role in bridging the gap between data science and production systems. While data scientists focus on model accuracy and experimentation, engineering teams prioritize scalability, performance, and reliability. MLOps aligns these objectives by introducing standardized workflows, automation, and governance across the ML lifecycle.
The importance of MLOps lies in its ability to:
- Reduce time-to-market for ML models
- Improve collaboration between teams
- Ensure model reproducibility and traceability
- Enable continuous monitoring and improvement
- Maintain compliance, security, and data governance
Without MLOps, machine learning projects often struggle with deployment failures, model drift, and operational inefficiencies.
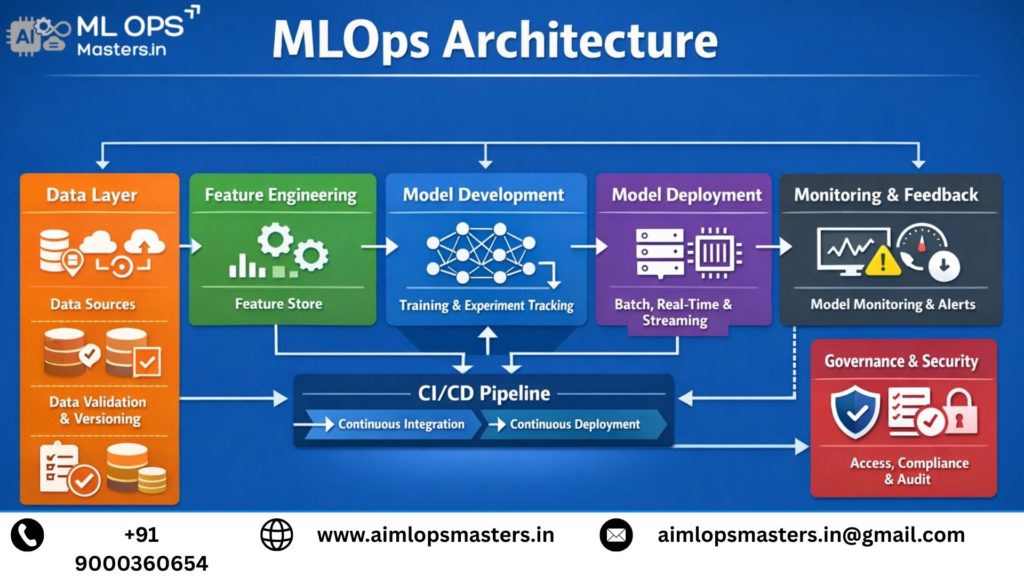
Key Components of MLOps Architecture
A typical MLOps architecture consists of multiple interconnected layers that work together to support the ML lifecycle:
- Data Layer: Handles data ingestion, validation, storage, and versioning
- Feature Engineering Layer: Transforms raw data into meaningful features
- Model Training Layer: Supports experimentation, training, and evaluation
- Model Registry: Stores and manages trained models with metadata
- Deployment Layer: Facilitates model serving through APIs or batch systems
- Monitoring and Feedback Layer: Tracks model performance, drift, and system health
Each component ensures that machine learning systems remain scalable, reliable, and maintainable in production environments.
- Data Layer: Handles data ingestion, validation, storage, and versioning
Data Management and Versioning in MLOps
Data forms the backbone of any machine learning system, making robust data management a critical pillar of MLOps architecture. MLOps promotes the design of well-structured and automated data pipelines that reliably handle data ingestion, validation, transformation, and storage. These pipelines ensure that high-quality, consistent, and timely data is available across development, testing, and production environments, thereby reducing the risk of errors and performance degradation in deployed models.
A key aspect of effective data management in MLOps is data versioning. By systematically tracking changes to datasets over time, teams can reproduce experiments with precision, compare model results across different data snapshots, and diagnose issues more efficiently. Data versioning also supports collaboration by providing transparency into how datasets evolve and how those changes impact model behavior.
Furthermore, maintaining clear lineage between raw data, engineered features, and trained models enables organizations to trace model outcomes back to their underlying data sources. This end-to-end traceability is essential for auditing, regulatory compliance, and governance, particularly in data-sensitive or regulated industries. By enabling better accountability and continuous feedback, strong data management practices within MLOps help organizations improve model performance, ensure trustworthiness, and sustain long-term machine learning success.

Model Development and Experimentation
Model development within an MLOps framework is designed to balance rapid experimentation with strong governance, reproducibility, and operational control. It provides data scientists with a controlled and collaborative environment where they can efficiently evaluate multiple algorithms, tune hyperparameters, and experiment with diverse feature sets, while ensuring that every change is systematically documented and traceable.
Experiment tracking plays a central role in this process. Specialized tools automatically record model configurations, training parameters, performance metrics, and generated artifacts such as model binaries and evaluation reports. This comprehensive logging enables objective comparison across experiments, supports informed decision-making, and allows teams to reproduce results reliably at any point in the future.
Once a model satisfies defined performance benchmarks and validation requirements, it is promoted through standardized and automated workflows into staging and production environments. These workflows enforce quality checks, approvals, and compliance policies, significantly reducing deployment risks. By combining structured processes with flexible experimentation, MLOps enables organizations to foster innovation while maintaining consistency, reliability, and confidence in their machine learning systems.
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) for Machine Learning
CI/CD in MLOps extends traditional DevOps practices to machine learning workflows. Continuous Integration ensures that changes to data pipelines, training code, or models are automatically tested and validated. This helps detect issues early and maintain code quality.
Continuous Deployment automates the release of validated models into production environments. Models can be deployed using strategies such as canary releases or blue-green deployments to minimize downtime and risk. CI/CD pipelines also support continuous retraining and model updates, enabling systems to adapt to changing data patterns and business requirements.
Introduction to MLOps Architecture
MLOps architecture provides a structured and systematic framework that allows organizations to design, deploy, monitor, and manage machine learning models efficiently within production environments. By integrating proven best practices from DevOps, data engineering, and machine learning, it establishes a unified approach to handling the complexities of modern ML systems.
A well-defined MLOps architecture ensures scalability by supporting distributed training, automated deployments, and seamless integration with cloud and on-premise infrastructure. It enhances reliability through standardized workflows, automated testing, continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD), and real-time monitoring of model performance and data behavior. Additionally, it promotes repeatability by enforcing version control for data, code, and models, enabling consistent and reproducible outcomes across different environments.
By reducing manual intervention and operational overhead, MLOps architecture significantly lowers system complexity and mitigates risks associated with deploying machine learning solutions at scale. It accelerates the transition from research and experimentation to real-world applications, empowering organizations to deliver high-quality, trustworthy, and business-ready ML models with greater speed and confidence.
Core Principles of MLOps
MLOps is built on a set of core principles that guide the development and operation of machine learning systems:
- Automation: Automating data pipelines, model training, testing, and deployment to minimize manual intervention
- Reproducibility: Ensuring experiments, models, and results can be consistently reproduced
- Scalability: Supporting increasing data volumes, users, and model complexity
- Monitoring and Feedback: Continuously tracking model performance, data drift, and system health
- Collaboration: Enabling seamless coordination between data scientists, ML engineers, and operations teams
These principles ensure that ML systems remain robust, transparent, and adaptable.
- Automation: Automating data pipelines, model training, testing, and deployment to minimize manual intervention
Data Management in MLOps
Data management is a cornerstone of MLOps architecture, providing the foundation upon which reliable and scalable machine learning systems are built. It encompasses the entire data lifecycle, including ingestion from multiple sources, validation and quality checks, preprocessing and transformation, secure storage, and systematic versioning. Well-designed data pipelines ensure that machine learning models are trained, tested, and evaluated on accurate, consistent, and up-to-date datasets, thereby improving model performance and stability in production.
Data versioning and lineage tracking are critical capabilities within this framework. By maintaining a clear record of how datasets evolve over time and how they are used across features and models, teams can precisely assess the impact of data changes on model outcomes. This transparency is essential for effective debugging, regulatory auditing, and compliance requirements, especially in environments where accountability and traceability are mandatory.
In addition, strong data management practices enable feature reuse and standardization across projects, reducing redundant work and improving collaboration between teams. By centralizing data assets and enforcing governance policies, organizations can build greater trust in their machine learning systems while accelerating development cycles and ensuring long-term operational efficiency.

Model Development Lifecycle
The model development lifecycle in MLOps encompasses experimentation, training, evaluation, and model selection. Data scientists explore different algorithms, features, and hyperparameters while tracking experiments and performance metrics.
Once a model meets predefined quality thresholds, it is registered and promoted through environments such as development, staging, and production. Standardized workflows ensure that only validated and approved models are deployed, reducing risk and improving operational stability.
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) for ML
CI/CD for machine learning extends traditional DevOps pipelines to include ML-specific workflows. Continuous Integration validates changes in code, data pipelines, and model configurations through automated testing. This ensures system integrity and consistency.
Continuous Deployment automates the release of models into production, enabling faster and more reliable updates. Advanced deployment strategies, such as canary releases and rollback mechanisms, help mitigate risk. CI/CD pipelines also support continuous training, allowing models to evolve with changing data and business requirements.
Introduction to MLOps and Its Importance
MLOps (Machine Learning Operations) is a set of practices that unifies machine learning development with operational workflows to ensure reliable, scalable, and efficient deployment of ML models. As machine learning systems increasingly influence business decisions, the need for consistency, traceability, and governance becomes critical. MLOps addresses these needs by introducing automation, monitoring, and collaboration across the ML lifecycle, with data management serving as its foundation.
Key Components of MLOps Architecture
Monitoring and logging function as integral components within a comprehensive MLOps architecture, seamlessly interacting with data ingestion pipelines, feature engineering workflows, model training environments, model registries, deployment platforms, and continuous feedback loops. Collectively, these elements establish a robust and scalable framework that ensures machine learning models are developed, deployed, and maintained in a consistent and reliable manner across their lifecycle.
Within this ecosystem, the monitoring layer provides real-time visibility into both model behavior and underlying system performance. It continuously tracks key indicators such as prediction accuracy, data drift, latency, resource utilization, and service availability. By proactively identifying deviations from expected behavior, monitoring enables early detection of performance degradation, operational issues, or changes in data patterns that may negatively impact model outcomes. This proactive oversight is essential for maintaining model reliability in dynamic, production-grade environments.
Complementing monitoring, logging captures detailed and structured records of system events, model predictions, input features, errors, and user interactions. These logs serve as a historical source of truth, supporting traceability and reproducibility throughout the ML lifecycle. Logging is particularly critical for root cause analysis, compliance audits, model debugging, and post-incident reviews, as it allows teams to reconstruct past system states and decision paths with precision.
Together, monitoring and logging empower organizations to make informed, data-driven decisions about model retraining, rollback, optimization, and governance. They form the foundation for transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement in MLOps, ensuring that machine learning systems remain performant, trustworthy, and aligned with evolving business and regulatory requirements.

Monitoring Metrics for Machine Learning Models
Monitoring in MLOps extends well beyond conventional infrastructure and application metrics, placing a strong emphasis on model-specific performance indicators that directly reflect the quality and reliability of machine learning outcomes. Core evaluation metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score provide insights into predictive effectiveness, while operational metrics like latency and throughput measure how efficiently models respond under real-world workloads. Together, these metrics ensure that models not only perform well statistically but also meet production-level performance expectations.
In addition to model performance, data-centric monitoring plays a critical role in sustaining long-term reliability. Metrics related to data drift, shifts in feature distributions, and changes in prediction confidence help identify discrepancies between training data and live production data. Since machine learning models are highly sensitive to data characteristics, even subtle changes in input patterns can lead to significant performance degradation if left unaddressed.
Concept drift detection further strengthens the monitoring framework by identifying changes in the underlying relationship between input features and target outcomes over time. Such shifts often occur due to evolving user behavior, market dynamics, or external factors. By continuously tracking these indicators, MLOps teams can proactively trigger alerts, initiate model retraining, adjust thresholds, or roll back deployments as needed. This continuous monitoring approach ensures sustained model performance, reinforces trust in automated decisions, and supports the delivery of reliable, high-quality machine learning systems in dynamic production environments.
Logging Best Practices in Machine Learning Workflows
Logging in MLOps entails the systematic and consistent capture of information across the entire machine learning lifecycle, serving as a critical foundation for transparency, reproducibility, and governance. This process encompasses detailed records from data ingestion pipelines, feature transformation steps, model training configurations, hyperparameters, evaluation results, and inference outputs generated in production. By maintaining comprehensive and well-organized logs at each stage, teams gain clear visibility into how data is processed, how models are built, and how predictions are produced.
Well-structured logging significantly simplifies troubleshooting and root cause analysis by enabling engineers and data scientists to trace issues back to specific pipeline stages or configuration changes. It also supports experiment reproducibility, allowing teams to reliably recreate past training runs and validate results. From a governance and compliance perspective, logs provide an auditable trail of model decisions and system behavior, which is increasingly important in regulated and high-stakes domains.
To maximize effectiveness, MLOps logging should follow established best practices. These include adopting standardized logging formats for consistency, correlating logs across interconnected pipelines and services, and aggregating them in centralized logging platforms for efficient querying and analysis. At the same time, logging strategies must strike a balance between granularity and system performance. Capturing critical insights without excessive verbosity helps prevent unnecessary storage consumption and processing overhead, ensuring that logging remains both scalable and cost-effective while delivering meaningful operational value.
Tools and Technologies for Monitoring and Logging
A wide range of tools and technologies are available to support effective monitoring and logging within modern MLOps environments. These tools are designed to operate across distributed and dynamic systems, providing continuous visibility into infrastructure health, model behavior, and data quality. Monitoring solutions focus on tracking system-level metrics such as resource utilization and availability, alongside model-centric indicators including performance metrics, latency, and data or concept drift. This dual focus ensures both operational stability and predictive reliability.
Complementing monitoring, logging platforms play a critical role in aggregating, storing, and analyzing logs generated by various components of the machine learning pipeline. These platforms consolidate logs from data pipelines, training workflows, deployment services, and inference endpoints, enabling teams to efficiently search, correlate, and analyze events across the system. This centralized view is essential for debugging, auditing, and understanding complex interactions in distributed ML architectures.
Commonly adopted solutions in this space include metrics monitoring systems, log aggregation and analysis platforms, experiment tracking tools, and specialized model observability frameworks. Experiment tracking tools help capture training parameters, metrics, and artifacts, while observability frameworks provide deeper insights into model predictions and behavior in production. When integrated effectively, these technologies deliver end-to-end visibility across the ML lifecycle, empowering teams to detect issues early, perform proactive maintenance, and continuously optimize models and pipelines. This holistic tooling approach is fundamental to building scalable, reliable, and production-ready machine learning systems.
Conclusion
Monitoring and logging are foundational pillars of MLOps, playing a critical role in ensuring that machine learning models remain accurate, reliable, and compliant throughout their production lifecycle. As models operate in dynamic real-world environments, continuous oversight is essential to verify that performance expectations are consistently met and that system behavior aligns with business and regulatory requirements.
By tracking meaningful model, data, and system metrics, organizations can gain early visibility into performance degradation, data drift, or operational anomalies. Robust logging practices further enhance this capability by providing detailed, auditable records of data processing, model decisions, and system events. Together, these practices enable faster issue detection, effective root cause analysis, and informed decision-making around model retraining, optimization, or rollback.
Leveraging the right combination of monitoring and logging tools allows teams to achieve end-to-end observability across the machine learning lifecycle. A mature and well-integrated monitoring and logging strategy not only improves operational resilience and model performance but also builds trust in AI-driven systems. Ultimately, it is a key enabler of sustainable, scalable, and responsible machine learning operations.
